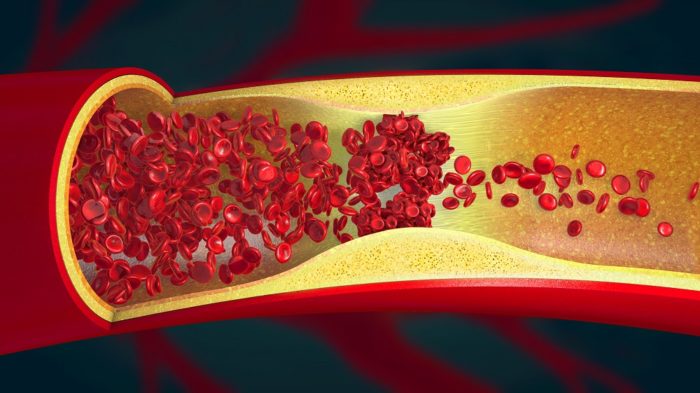
About 795,000 people in the United States suffer from a stroke each year. This medical emergency occurs when a clot blocks the blood supply to your brain, causing a blood vessel to burst. Brain cells will die within minutes after this incident, so prompt medical attention is crucial to saving an individual’s life.
Knowing more about this vascular concern can help you take action quickly in the event of this emergency. Read on to learn about the symptoms, recovery, and prevention of strokes from your local cardiovascular specialist.
What Does a Stroke Look Like?
People of any gender can have similar symptoms during a stroke. These may include sudden numbness, especially on one side of the body; confusion or speech issues; vision or movement problems; or a severe headache.
Call 911 immediately if you or someone near to you has any of these problems. Quick treatment of this problem could save a patient from brain damage or death. To check if a person might be having a stroke, you can consider the acronym F.A.S.T.
- Face: Ask the patient to smile and note if one side appears to droop.
- Arms: Ask the patient to lift both arms and see if one arm appears to be lower than the other.
- Speech: Ask the patient to repeat a phrase and check for slurring or other speaking abnormalities.
- Time: This emphasizes that you need to call 911 right away if any of these symptoms are present in the patient.
What Is Recovery from a Stroke Like?
A stroke is a medical emergency, so the patient can expect treatment for the problem in a hospital. The doctor might give the patient a medication that will break up the blood clot if they get to the hospital quickly. In some cases, doctors will repair ruptured blood vessels with surgery.
Patients may notice weakness or paralysis, cognitive problems, and other symptoms following their stroke. Depending on their unique case, the patient can begin rehabilitation in the hospital and then transition to their home or a facility, where they will continue exercises to regain physical and speech abilities. Recovery will look different for each patient. Ask your doctor for details about what you can expect as you heal from this event.
Can I Prevent a Stroke?
If you have suffered a stroke, you will have a high risk of experiencing another one. To prevent a stroke, you should work with your doctor to treat underlying risk factors that could cause this emergency.
Your doctor may prescribe medicine to treat high blood pressure or high cholesterol. They may also suggest lifestyle changes, including dietary restrictions and exercise regimens, to lower the risk of a stroke.
If you have heart disease or an irregular heartbeat, your doctor will want to monitor these concerns and offer treatment as needed. They may want to do heart repair surgery to amend damaged cardiac tissue or to place an implantable cardioverter defibrillator in the chest to regulate your heartbeat.